2. Developer
The developer consists of water, developer, inhibitor, wetting agent, and the like.
The developer is the main agent of the developer and is used to dissolve the light decomposed part of the photosensitive layer of the PS plate. The commonly used strong alkali developer is NaOH, KOH (potassium hydroxide), and the weak alkali developer is Na2SiO3. To prepare the developer, different alkaline developers are selected according to the method of aluminum plate surface treatment and the thickness of the oxide film. For aluminum base strong alkali resistance, such as the base plate after anodizing, high temperature sealing treatment, oxide film thickness of 5g/m2, or plate base oxide film alkali resistance test, alkali resistance time of more than 50s PS plate, choose NaOH or KOH more, for aluminum plate base weaker alkali resistance, such as the plate base has not been anodized, only coated with hydrophilic material on the surface of aluminum plate, or base plate oxide film alkali resistance Sex test, PS plate with alkali resistance less than 50s, Na2SiO3 is mostly used. In addition to the development effect of Na2SiO3, there is a role of forming a hydrophilic film layer, buffering corrosion, not only makes the printing plate have a good hydrophilicity, but also has little solubility in the graphic part, which is a stable performance and service life. Long developer.
Inhibitors are used to suppress the speed of development. Because the aluminum oxide base film's oxide film has poor resistance to alkali, it is strongly recommended that it be formulated with developer. When used, the developing speed is very fast. In order to prevent the dissolution of the developer from the aluminum plate base, the developing speed must be reduced. The method is to develop Inhibitors are added to the solution. Commonly used inhibitors are KCl (potassium chloride), NaCl (sodium chloride), Na3PO4 (sodium phosphate), etc. KCl and its role in inhibiting the development speed, in addition to the role of auxiliary washing. If formulated with a developer, because Na2SiO3 itself has a corrosion inhibitory effect, no additional inhibitor is required.
The role of the wetting agent is to reduce the surface tension of the developer, increase the wettability of the developer, and evenly spread the developer onto the surface of the printing plate to facilitate uniform development. Common wetting agents include surfactants such as sodium dodecylbenzene phosphate and Tween. Sodium dodecylbenzene phosphate is an anionic surfactant and Tween is a trade name for sorbitan stearate polyoxyethylene ether, a nonionic surfactant. In addition to their wettability, these two surfactants also have emulsifying and dispersing properties, and they also help the printing plate in the development process.
The PS-versions produced by different manufacturers, the composition of the photosensitive layer, and the processing method of the plate base are all somewhat different, and their alkali resistance is also different. Therefore, the developer must be formulated with developers, inhibitors, wetting agents, and matching ratios based on the performance of the PS plate. Here are two commonly used developer solutions for reference during formulation.
Strong base dilute solution developer:
NaOH 1~4 g
Na3PO4 25g
Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate 1~2g
Water 1000ml
Weak alkali dilute solution developer:
Na2SiO3 3~6g
Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate 1~2g
Water 1000ml.
The higher the content of the developer in the developer, the faster the development. If the development is excessive, the photosensitive layer without light will be dissolved, the percentage of the dots on the printing plate will be reduced, the grease of the plate and the resistance of the printing plate will be reduced. Even "off version" failure; the other hand, the lower the developer content, the slower the development speed, which not only to extend the development time, but also due to lack of development, resulting in an increase in the percentage of outlets, layout dirty. The content of the developer is usually determined according to the developer formulation provided by the manufacturer of the PS plate. However, since the development conditions have a direct influence on the development quality, the test development must be performed under a fixed development condition before the final development. Developer concentration. The development tolerance of domestically-made positive-working PS plates is generally 2 minutes. In order to accurately control the concentration of the developer, a PS plate with a printing plate may be developed for 30 to 60 seconds, and then a magnifying glass 30 to 50 times larger. Observe that if the hollow spot of the 98 to 99% ruler of the printing plate does not stick, and 1 to 2% of the small black spots are not lost, the developer concentration is appropriate.
Third, the development operation
Mechanical development is performed using an automatic developing machine. There are many types of automatic developing machines, but their structures are basically the same. They are composed of a liquid temperature control device, a speed adjustment device, and a circulation device for developing and other rinsing liquids. Various solutions to the layout of the role and circulation are carried out in their separate discrete slots, there can be no leakage between each other. FIG. 7 is a schematic view of a structure of an automatic developing machine that is currently widely used. Development and processing are performed by using a spray pipe to spray liquid onto a plate, followed by brushing.
The efficiency of the automatic developing machine is very high. A class (8 hours) can process more than 30 plates, and the development quality is also very stable. However, the developer will generally be aged during use. The aging phenomenon of the developer refers to a phenomenon in which the developing solution gradually fades in the process of continuously processing a large number of printing plates until it completely disappears. This aging phenomenon is the result of developing the developer for a long time. For the alkaline developer, it also absorbs NaOH in the developer.
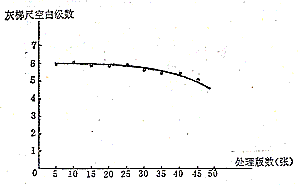
The occurrence of neutralization is related to the reaction. The ageing phenomenon of the developer can be observed on the gray scale stamped under the same exposure conditions when observing the blank progression (Fig. 8). Due to the effect of ageing of the developer, the number of plates that are qualified for development in production is limited, which requires a predetermined number of plates as a standard. The number of developed plates exceeds this standard, and the developer must be updated. The specific method for determining the standard printing plate number is as follows: The PS plate is cut into small pieces, and each block has a grey ladder ruler and a dot ladder ruler (or printing ruler ruler), and is printed under the same conditions to make a test block. (The quantity meets the test requirement, generally about 40-50 pieces) Stored in a place that is protected from light and not affected by temperature and humidity. Starting from a new developer filled with an automatic developing machine, a test is developed at a certain time interval. The version is used to check the step change and dot reproducibility of the gray ladder rule, and record the number of developed plates and the step change and dot change of the gray scale on the test plate; the qualified results can be determined based on the above test results. Version of the standard plate number, and then determine the time to update the developer. For example, when the gray ladder is lowered by one step, 45 plates are developed and processed. If the number is defined as the development standard, the developer should be updated once for each 45 plates developed (Fig. 8).
The developer consists of water, developer, inhibitor, wetting agent, and the like.
The developer is the main agent of the developer and is used to dissolve the light decomposed part of the photosensitive layer of the PS plate. The commonly used strong alkali developer is NaOH, KOH (potassium hydroxide), and the weak alkali developer is Na2SiO3. To prepare the developer, different alkaline developers are selected according to the method of aluminum plate surface treatment and the thickness of the oxide film. For aluminum base strong alkali resistance, such as the base plate after anodizing, high temperature sealing treatment, oxide film thickness of 5g/m2, or plate base oxide film alkali resistance test, alkali resistance time of more than 50s PS plate, choose NaOH or KOH more, for aluminum plate base weaker alkali resistance, such as the plate base has not been anodized, only coated with hydrophilic material on the surface of aluminum plate, or base plate oxide film alkali resistance Sex test, PS plate with alkali resistance less than 50s, Na2SiO3 is mostly used. In addition to the development effect of Na2SiO3, there is a role of forming a hydrophilic film layer, buffering corrosion, not only makes the printing plate have a good hydrophilicity, but also has little solubility in the graphic part, which is a stable performance and service life. Long developer.
Inhibitors are used to suppress the speed of development. Because the aluminum oxide base film's oxide film has poor resistance to alkali, it is strongly recommended that it be formulated with developer. When used, the developing speed is very fast. In order to prevent the dissolution of the developer from the aluminum plate base, the developing speed must be reduced. The method is to develop Inhibitors are added to the solution. Commonly used inhibitors are KCl (potassium chloride), NaCl (sodium chloride), Na3PO4 (sodium phosphate), etc. KCl and its role in inhibiting the development speed, in addition to the role of auxiliary washing. If formulated with a developer, because Na2SiO3 itself has a corrosion inhibitory effect, no additional inhibitor is required.
The role of the wetting agent is to reduce the surface tension of the developer, increase the wettability of the developer, and evenly spread the developer onto the surface of the printing plate to facilitate uniform development. Common wetting agents include surfactants such as sodium dodecylbenzene phosphate and Tween. Sodium dodecylbenzene phosphate is an anionic surfactant and Tween is a trade name for sorbitan stearate polyoxyethylene ether, a nonionic surfactant. In addition to their wettability, these two surfactants also have emulsifying and dispersing properties, and they also help the printing plate in the development process.
The PS-versions produced by different manufacturers, the composition of the photosensitive layer, and the processing method of the plate base are all somewhat different, and their alkali resistance is also different. Therefore, the developer must be formulated with developers, inhibitors, wetting agents, and matching ratios based on the performance of the PS plate. Here are two commonly used developer solutions for reference during formulation.
Strong base dilute solution developer:
NaOH 1~4 g
Na3PO4 25g
Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate 1~2g
Water 1000ml
Weak alkali dilute solution developer:
Na2SiO3 3~6g
Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate 1~2g
Water 1000ml.
The higher the content of the developer in the developer, the faster the development. If the development is excessive, the photosensitive layer without light will be dissolved, the percentage of the dots on the printing plate will be reduced, the grease of the plate and the resistance of the printing plate will be reduced. Even "off version" failure; the other hand, the lower the developer content, the slower the development speed, which not only to extend the development time, but also due to lack of development, resulting in an increase in the percentage of outlets, layout dirty. The content of the developer is usually determined according to the developer formulation provided by the manufacturer of the PS plate. However, since the development conditions have a direct influence on the development quality, the test development must be performed under a fixed development condition before the final development. Developer concentration. The development tolerance of domestically-made positive-working PS plates is generally 2 minutes. In order to accurately control the concentration of the developer, a PS plate with a printing plate may be developed for 30 to 60 seconds, and then a magnifying glass 30 to 50 times larger. Observe that if the hollow spot of the 98 to 99% ruler of the printing plate does not stick, and 1 to 2% of the small black spots are not lost, the developer concentration is appropriate.
Third, the development operation
Mechanical development is performed using an automatic developing machine. There are many types of automatic developing machines, but their structures are basically the same. They are composed of a liquid temperature control device, a speed adjustment device, and a circulation device for developing and other rinsing liquids. Various solutions to the layout of the role and circulation are carried out in their separate discrete slots, there can be no leakage between each other. FIG. 7 is a schematic view of a structure of an automatic developing machine that is currently widely used. Development and processing are performed by using a spray pipe to spray liquid onto a plate, followed by brushing.
The efficiency of the automatic developing machine is very high. A class (8 hours) can process more than 30 plates, and the development quality is also very stable. However, the developer will generally be aged during use. The aging phenomenon of the developer refers to a phenomenon in which the developing solution gradually fades in the process of continuously processing a large number of printing plates until it completely disappears. This aging phenomenon is the result of developing the developer for a long time. For the alkaline developer, it also absorbs NaOH in the developer.
The occurrence of neutralization is related to the reaction. The ageing phenomenon of the developer can be observed on the gray scale stamped under the same exposure conditions when observing the blank progression (Fig. 8). Due to the effect of ageing of the developer, the number of plates that are qualified for development in production is limited, which requires a predetermined number of plates as a standard. The number of developed plates exceeds this standard, and the developer must be updated. The specific method for determining the standard printing plate number is as follows: The PS plate is cut into small pieces, and each block has a grey ladder ruler and a dot ladder ruler (or printing ruler ruler), and is printed under the same conditions to make a test block. (The quantity meets the test requirement, generally about 40-50 pieces) Stored in a place that is protected from light and not affected by temperature and humidity. Starting from a new developer filled with an automatic developing machine, a test is developed at a certain time interval. The version is used to check the step change and dot reproducibility of the gray ladder rule, and record the number of developed plates and the step change and dot change of the gray scale on the test plate; the qualified results can be determined based on the above test results. Version of the standard plate number, and then determine the time to update the developer. For example, when the gray ladder is lowered by one step, 45 plates are developed and processed. If the number is defined as the development standard, the developer should be updated once for each 45 plates developed (Fig. 8).
Next: three tests on cigarette packaging after WTO faces: bright chapter in Folli Follie personality
[News Search] [Add to Favorites] [Tell a friend] [Print this article] [Close window] Similar information
Total 0 [View All] Related Reviews
Sofa Collection,Best Living Room Furniture Sets,Furniture Sets,Sofa Collections
FOSHAN COOC FURNITURE CO.,LTD , https://www.coocfurniture.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)